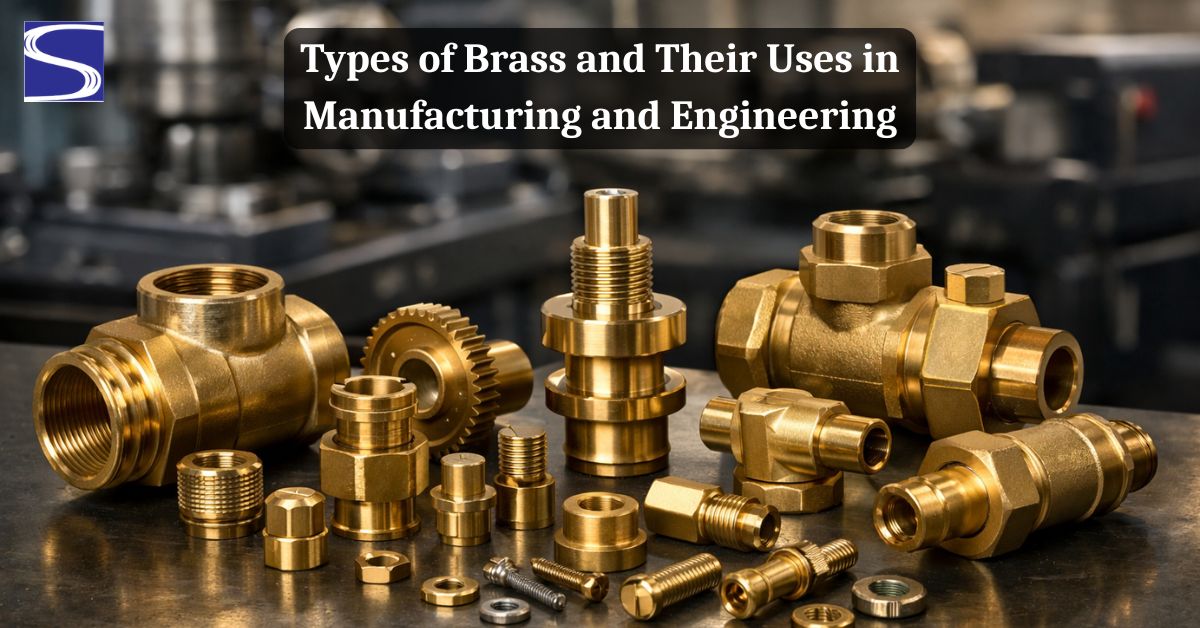
One of the many reasons Brass is one of the most frequently used alloys in engineering is because of its versatility and is also easily fabricated. Understanding the different types of brasses used across different industries aids engineers and manufacturers in choosing the best materials that suit different performance requirements. Brass is used in everything from precision machining to structural components and is still one of the most important materials used in manufacturing systems today.
India’s brass manufacturing ecosystem is strongly supported by Brass Manufacturers in Jamnagar, who are widely recognized for their expertise in precision machining, alloy consistency, and large-scale industrial production.
In order to evaluate its role in modern manufacturing systems, how many types of brass there are needs to be determined. The brass types along with the composition of each type must be examined to evaluate the types of brass.
What Is Brass Casting?
Brass casting involves pouring molten brass into a prepared casting and then after the brass is solidified, it is removed from the mold. The entire process results in the creation of a final component, and is helpful in creating components which are difficult to create through machining processes.
The brass metal casting process helps in the construction of highly complex structures that others methods cannot help with, thus it is highly beneficial for large manufacturing enterprises. It is also highly adaptable and with efficient construction. It is also the best for rather demanding applications as it possesses highly uniform construction properties.
Understanding Brass as an Engineering Alloy
The different alloys that make up these different types of brasses result in the varying mechanical and physical properties of the alloy. Brass is a copper-zinc alloy and the different copper and zinc compositions, as well as any added trace elements, will result in an alloy optimized for one of the three qualities of strength, conductivity, or formability.
In order to satisfy the stringent dimensional and environmental requirement, especially in the electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and fluid control systems, the engineering professionals rely on the different types of brass alloys available in the market.
How Many Types of Brass Are There?
In any classification scheme, the first question is usually how many types of brass are there? The classification of brass alloys is a result of the zinc content and the microstructure. Such classifications provide a way for the engineers to position the alloys and the associated performance parameters.
In the field, brass alloys are typically described as alpha, alpha-beta, and beta brasses. Each of these different classifications serves a unique engineering and manufacturing purpose. Knowing how many types of brass are there helps in making the right alloy choice to suit engineering design and materials selection for the component.
Types of Brass and Their Composition
The different types of brass and composition of brass alloys determine their mechanical strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Performance may differ even with small variations in the percentage of zinc.
Alpha Brass
Among all the brass types, Alpha brass generally contains less zinc and hence has more copper content. Alpha brass is very ductile and is quite suitable for cold working. Among the different types of brass, Alpha brass is quite used for the making of a lot of components.
Alpha-Beta Brass
There is a fair amount of balance in the copper and zinc content which results in a fair degree of strength and workability. The composition of the types of brass in this subsection support both hot and cold processes on the formed parts which makes them ideal for use in making industrial components that can be subjected to reasonable moderate loads.
Beta Brass
Beta brass is more strong and rough than other types of brass. That is because their zinc concentration is higher than others. They are usually hot-worked and thus, are more mechanically strong, but not as ductile.
Common Types of Brass Material Used in Industry
Manufacturing industries rely on specific types of brass material designed for precise functional needs.
Free-Cutting Brass
In Brass, including lead is said to increase the brass’s machinability. This is used often in CNC operations and in components that have a very high precision and the tolerances are very tight.
Naval Brass
Naval brass contains tin which improves corrosion resistance, especially in marine and high-moisture applications. This alloy is one of the various types of brass which is suited for the more demanding applications.
Cartridge Brass
This brass type is known for its cold-working capabilities. Therefore, cartridge brass is used in deep drawn components. This types of brass material is suited for applications involving repeated forming to great extents.
Brass Alloys is a very detailed and sophisticated resource that explains the variation of performance in terms of the behavior of alloy, and in it in the manner of the understanding of the manufacturing industries.
Different Types of Brass and Their Uses in Manufacturing
For the processes of making things by using brass, including in the processes of machining, the various types of brass that are available should be tailored to specific needs.
- Machining needs alloys that can manage chips effectively.
- Casting has fluidity and dimensional stability.
- Electrical parts need to have good conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Precision machined parts such as fittings, connectors, and fasteners are made from certain types of brass that are engineered to be dimensionally stable. The production of quality brass precision parts requires appropriate alloy selection for consistent quality throughout production runs.
Types of Brass Used in Engineering Applications
Engineering fields require specific brass types that address performance and safety criteria.
Mechanical Engineering
Brass is used for bushings, gears, and threaded parts because of the low friction and wear resistance of the material. There is often consideration of how many types of brass are there for selection of the best alloy for components that bear loads.
Electrical Engineering
Brass used for terminals and connectors provides good conductivity and resistance to corrosion. The various types of brass used in these applications ensure consistent performance in electrical applications.
Plumbing and Fluid Control
Valves, nozzles, and fittings require corrosion resistance and pressure stability. These applications rely heavily on specialized types of brass material engineered for long-term durability.
A structured overview of alloy classifications can be explored further through Types of Brass Materials.
Selecting the Right Type of Brass for Industrial Use
There are a few things to consider when choosing a type of brass:
- What are the mechanical strength requirements?
- Is it going to be exposed to moisture, or is it going to be exposed to chemicals?
- What machining, or forming, method are you going to use?
- Is it cost efficient, and is it readily available?
By understanding the types of brass and their composition, when manufacturers understand how every type of brass is different, they can reduce material failure and improve the longevity of the product. Balanced, and strategic, alloy selection will ensure all production methods and operational environments are met.
Role of Precision Engineering in Brass Manufacturing
The use of brass types to its fullest extent is highly reliant on precision engineering. The most advanced machining, alloy control, and surface finishing processes allows for control of dimension and consistency.
This is especially true when talking about industries that require high tolerance and precision. Engineering expertise is a must, as is explained in Advantage in Brass Engineering, when material science and precision manufacturing come together.
Conclusion
The modern merging of engineering and manufacturing relies on knowing how to use different types of brass for different applications. The right brass can be the difference in how well the piece performs, how efficient the piece is, and how long it lasts. Engineers need to take the time to research the various types of brass, understand how each type is different, and consider the composition and the application to make the right decision on materials for a dependably scalable production system.